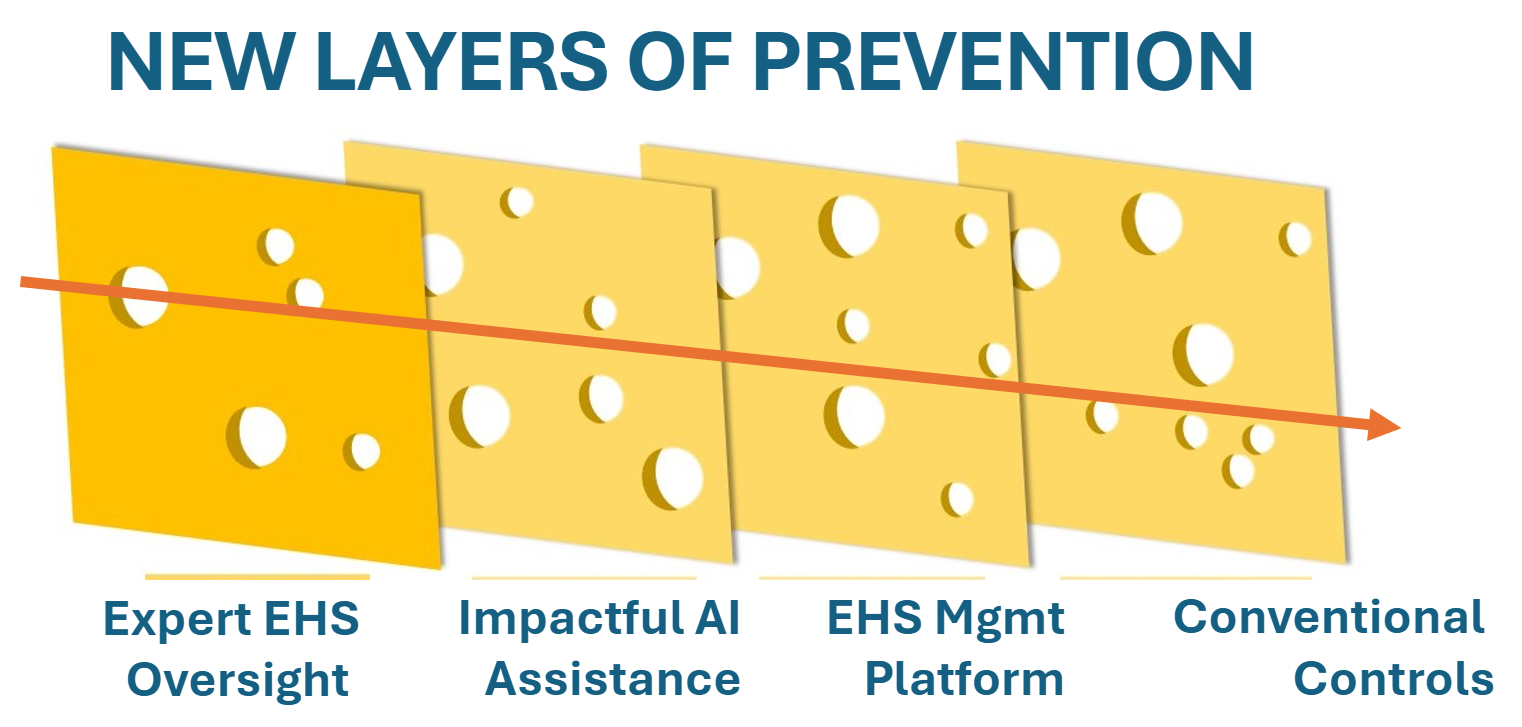
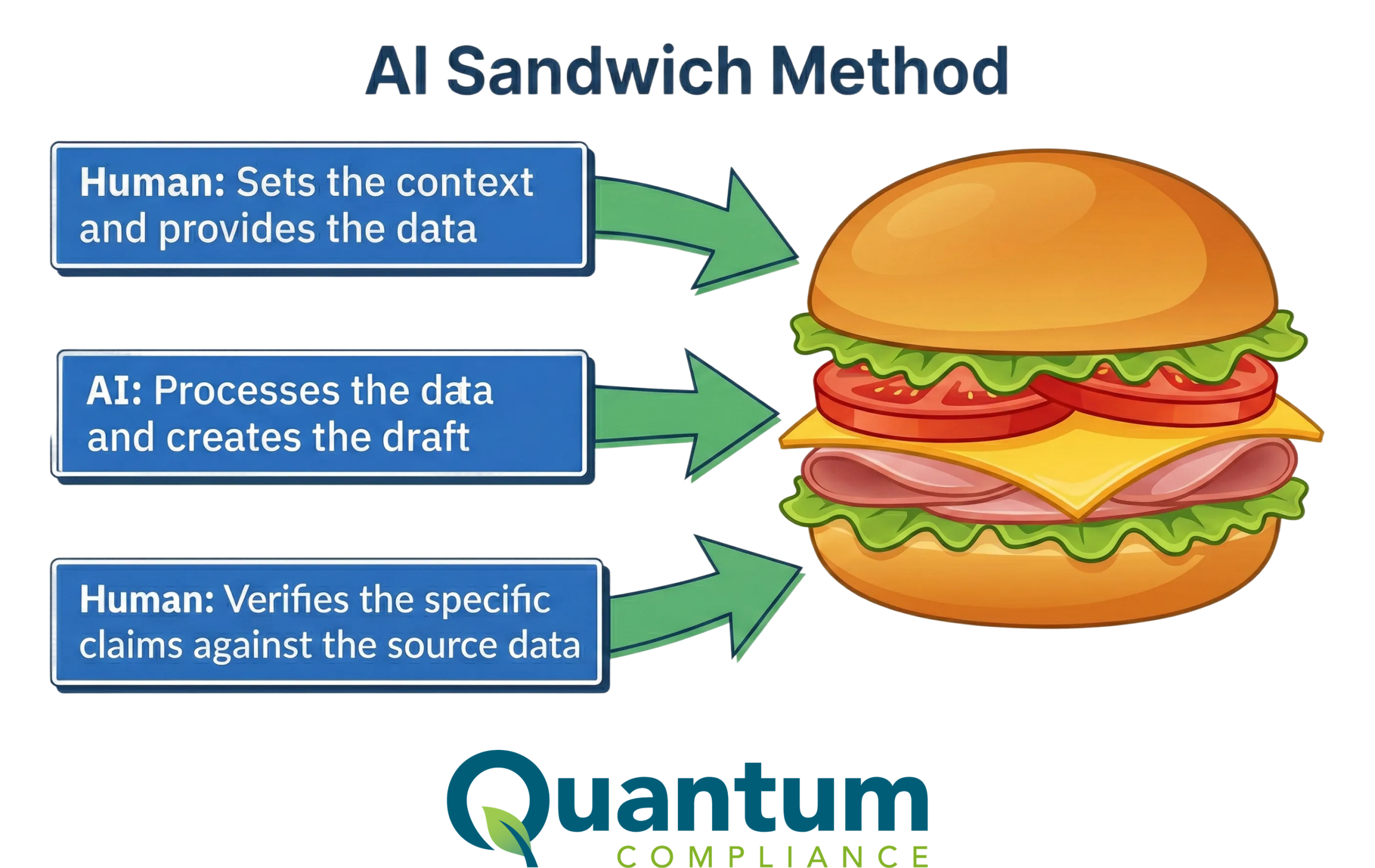
Form 300 Reporting is a critical aspect of maintaining workplace safety and compliance with OSHA regulations. However, the process of recording and classifying work-related injuries and illnesses can be fraught with challenges. Navigating these challenges effectively is essential to ensure accurate and compliant reporting. Here are some common pitfalls in Form 300 Reporting and strategies to avoid them.
Pitfall 1: Incomplete or Inaccurate Data
One of the most common issues in Form 300 Reporting is the entry of incomplete or inaccurate data. Missing or incorrect information can lead to non-compliance with OSHA regulations and obscure the true nature of workplace safety issues.
How to Avoid It:
- Training: Provide comprehensive training for employees and supervisors on how to accurately report incidents and fill out Form 300.
- Checklists: Use checklists to ensure all required fields are completed correctly.
- Review Process: Implement a review process where a second person verifies the data before it is finalized.
Pitfall 2: Delayed Reporting
Timeliness is crucial in Form 300 Reporting. OSHA requires that recordable injuries and illnesses be recorded within seven calendar days of receiving information about the incident. Delays can lead to compliance issues and reduce the accuracy of the data.
How to Avoid It:
- Automated Notifications: Use incident reporting systems that send automatic reminders to ensure timely reporting.
- Real-Time Data Entry: Implement systems that allow for real-time data entry to capture incident details immediately.
- Clear Reporting Protocols: Establish clear protocols and deadlines for reporting incidents.
Pitfall 3: Misclassification of Incidents
Misclassifying incidents on Form 300 can lead to inaccurate records and potential compliance issues. It’s important to understand the criteria for what constitutes a recordable injury or illness.
How to Avoid It:
- Training and Guidelines: Provide training and clear guidelines on how to classify different types of incidents.
- Reference Materials: Keep reference materials handy that outline OSHA’s classification criteria.
- Consultation: When in doubt, consult with safety professionals or use automated tools that guide classification decisions.
Pitfall 4: Lack of Consistency
Inconsistencies in how incidents are reported and recorded can undermine the effectiveness of Form 300 Reporting. This can occur when different employees handle reporting differently or when there is a lack of standardized procedures.
How to Avoid It:
- Standardized Procedures: Develop and enforce standardized procedures for reporting and recording incidents.
- Consistent Training: Ensure that all employees receive the same training and understand the importance of consistency.
- Centralized Reporting System: Use a centralized reporting system to ensure uniform data entry and record-keeping.
Pitfall 5: Failing to Post the Annual Summary
OSHA requires employers to complete and post the OSHA Form 300A, the “Summary of Work-Related Injuries and Illnesses,” annually. Failing to post this summary can result in non-compliance and penalties.
How to Avoid It:
- Reminders and Alerts: Set reminders and alerts to ensure that the Form 300A summary is completed and posted on time.
- Visibility: Post the summary in a visible location where employees can easily see it, as required by OSHA regulations.
- Record Keeping: Maintain copies of posted summaries for your records and compliance verification.
Pitfall 6: Poor Record Maintenance
Maintaining accurate and accessible records is essential for compliance and effective workplace safety management. Poor record maintenance can lead to lost or incomplete records, making it difficult to track and analyze incident data.
How to Avoid It:
- Digital Records: Use digital systems to store and manage Form 300 records, ensuring they are easily accessible and secure.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of your records to ensure they are complete and up-to-date.
- Backup Systems: Implement backup systems to protect against data loss.
Pitfall 7: Inadequate Employee Access
Employees, former employees, and their representatives have the right to access the Form 300 log. Inadequate access can lead to compliance issues and a lack of transparency.
How to Avoid It:
- Easy Access: Ensure that Form 300 logs are easily accessible to those who have the right to view them.
- Clear Communication: Communicate clearly to employees about their rights to access these records.
- Electronic Access: Provide electronic access to the logs to facilitate easy viewing.
Conclusion
Navigating the challenges in Form 300 Reporting requires a proactive approach to avoid common pitfalls. By ensuring accurate and timely data entry, providing comprehensive training, using standardized procedures, and leveraging technology, employers can enhance their Form 300 Reporting process. Avoiding these common pitfalls not only ensures compliance with OSHA regulations but also contributes to a safer and healthier workplace. Effective Form 300 Reporting is a critical tool in the ongoing effort to improve workplace safety and protect employees from work-related injuries and illnesses.